IGN reports another 3.3 magnitude earthquake in the Canary Islands
- 18-10-2024
- Gran Canaria
- INVOLCAN .
- Photo Credit: IGN
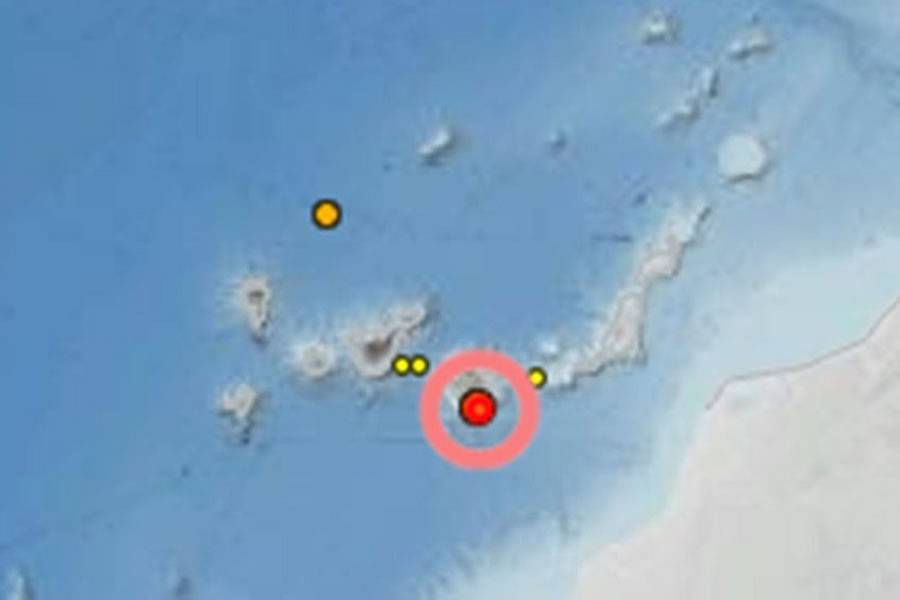
The National Geographic Institute (IGN) has reported a 3.3 magnitude earthquake in the Canary Islands, at 2:46pm yesterday, Thursday, October 17th, with its epicentre located in the region of Santa Lucía de Tirajana, on the south coast of Gran Canaria.
According to data from the IGN, the earthquake occurred at a depth of 27 kilometres, at the coordinates of 27.6774° latitude north and -15.5442° longitude west.
While the earthquake's magnitude is considered moderate, it was felt in some nearby areas, as reported in initial observations from residents.
This seismic event is the latest in a series of tremors recorded in the Canary Islands. The archipelago is under constant seismic monitoring due to its active geological dynamics. Ongoing studies are being conducted to better understand the tectonic activity of the region, which has seen increasing seismic activity in recent years.
Local authorities have not reported any significant damage, and the event serves as a reminder of the island’s natural susceptibility to seismic occurrences, urging residents to stay informed and prepared.
Who are the IGN?
The Instituto Geográfico Nacional, or IGN, is a Spanish government agency responsible for producing and maintaining geographical, cartographic, and geospatial data for Spain, which includes the Canary Islands.
Founded in 1870, IGN plays a crucial role in the country's infrastructure and development by providing accurate maps, geographic information, and geospatial services.
Here are the main functions and responsibilities of the IGN:
1. Cartography and Mapping: IGN produces and updates official maps of Spain, both in digital and printed formats. This includes topographic maps, road maps, and thematic maps for various purposes such as land use, population distribution, and environmental planning.
2. Geodesy: IGN manages geodetic networks, which provide the reference points and systems for accurate positioning and measurements across Spain. This is crucial for civil engineering, GPS, and other location-based services.
3. Geographical Information Systems (GIS): IGN develops and maintains geospatial databases and provides tools for users to access and utilize this information for various applications, from urban planning to environmental conservation.
4. Natural Disaster Monitoring: The institute is involved in monitoring and studying natural hazards, such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and tsunamis. Its National Seismic Network (Red Sísmica Nacional) is responsible for tracking and reporting seismic events in Spain and surrounding regions.
5. Aerial Photography and Remote Sensing: IGN collects aerial photographs and satellite imagery, which are used for updating maps, environmental monitoring, and urban planning.
6. Geographical Names and Boundaries: It ensures the official naming and standardisation of geographical features, such as mountains, rivers, and cities. It also oversees the establishment and maintenance of Spain's official boundaries.
7. Research and Development: The IGN engages in scientific research to improve geographic and geodetic methods and technologies, supporting innovation in spatial data analysis, remote sensing, and earth observation.
As part of Spain's Ministry of Transport, Mobility, and Urban Agenda, the IGN collaborates with various regional and international organisations to ensure the standardisation and quality of geospatial information both in Spain and globally.
Other articles that may interest you...
Trending
Most Read Articles
Featured Videos
TributoFest: Michael Buble promo 14.02.2026
- 30-01-2026
TEAs 2025 Highlights
- 17-11-2025